Creation
Creation
Strictly speaking, these are not "operators" in the conventional sense, because they create new IceImage instances. They are accessed from the scripting language by sending the class name IceImage the messages below. This would be analogous to using a static member function in C++.
All these operations create a leaf node: a node with no inputs forming the leaves of an image processing expression.
For more information on how to use IceMan with "it", check out the "it" scripting tutorials: Introduction to "it" Scripting, More "it" Scripting, IceMan Scripting and Tcl, and Custom "it" Save スクリプト.
Note
The examples provided below are the IceMan expressions as they would be used in the "it" console, using Python. You can also use help() to get more details on a specific operator. For example:
py> help(ice.PolyFill) Help on built-in function PolyFill in module ice._ice: PolyFill(...) Create an image with a filled polygon. Edges are anti-aliased using a super-sampling grid specified in samples. (5, 5) is usually sufficient. i = ice.PolyFill(colorCard, pointList, samples) py>Note2
Some of the operators below take a "box" (image rectangle) list as an input parameter. The format of the list should be [xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax].
Card(type, [sample1, ... ,sampleN])
Create a card, or an image of constant color. Cards are evaluated upon creation, unlike other images.
サンプル
grey = ice.Card(ice.constants.FLOAT, [0.5]) red = ice.Card(ice.constants.FLOAT, [1,0,0]) redalpha = ice.Card(ice.constants.FLOAT [1,0,0,1])
FilledImage(type, box, color)
Create an image of a specified type and size that's filled with a specified color. This is like a card, except that it has finite dimensions, and is not allocated until used.
Example

box = [0, 300, 0, 200] color = [1.0, 0.5, 0.3, 1.0] p = ice.FilledImage(ice.constants.FLOAT, box, color)
GaussianNoise(type, ply, box, muAndSigma, range, seed)
Create an image filled with Gaussian noise in the specified range. Mean and standard deviation are specified as a pair of floating point values.
Example

box = [0, 300, 0, 200] musig = [0.5,0.25] range = [0, 1.0] p = ice.GaussianNoise(ice.constants.FRACTIONAL, 3, box, musig, range, 321234)
PolyFill(color, pointList, samples)
Create an image with a filled polygon. Edges are anti-aliased using a super-sampling grid specifed in samples. [5, 5] is usually sufficient.
Example

color = ice.Card(ice.constants.FLOAT, [1.0, 0.5, 0.3]) vertices = [(228,343), (387, 218), (478, 357), (682, 233), (746, 338), (778, 450), (629, 547), (391, 545), (388, 348), (322, 331), (275, 398), (189, 386)] samples = [5, 5] p = ice.PolyFill(color, vertices, samples)
UniformNoise(type, ply, box, range, seed)
Create an image filled with values uniformly distributed in the specified range.
Example

size = [0, 300, 0, 200] range = [0.4, 0.6] seed = 398493 p = ice.UniformNoise(ice.constants.FRACTIONAL, 3, size, range, seed)
Ramp(type, ply, box, angle, center, width, clampVal, easeInOut)
This is a function to create a general color ramp. The angle is specified in degrees from the vertical. The center of the ramp is where the pixel value is exactly half-way between minimum and maximum values. The width is specified in pixels along the direction of variation. The range of values in the ramp is restricted to clampVal. The parameter easeInOut contains the ease-in point, below which the ramp smoothly reduces to the minimum value, and the ease-out point, above which the ramp smoothly "decelerates" to the maximum value. Ease-in/out points are expressed as fractions of the total ramp width.
In the example shown below, the angle of the ramp is 32.3, its center is at pixel coordinates [150.6, 100.1], its width is 363.4 pixels, its values are clamped between 0 and 0.85, and the ease-in and ease-out points are 36.34 pixels from either end of the ramp.
Example

size = [0, 300, 0, 200] center = [156.2, 100.1] minAndMax = [0, 0.85] ease = [0.1, 0.1] p = ice.Ramp(ice.constants.FLOAT, 3, size, 32.3, center, 363.4, minAndMax, ease)
RBFInterp(dataBox, pointList, valueTable, rFrac, freezeEdges)
Given the values of a function f(x, y) at arbitrary points on the 2D pixel planes, compute values for all points on the pixel grid by radial basis function interpolation.
Example

size = [0, 300, 0, 200] centers = [(10, 10), (50,50), (200,100)] valuesAtCenters = [0.4, 0.6, 0.8] sphereOfInfluence := .5 freezeEdges := 0 p = ice.RBFInterp(size, centers, valuesAtCenters, sphereOfInfluence, freezeEdges)
Sparkle(sparkleType, imageSize, center, type, slitAngle)
Sparkle and glow kernels for selective convolution. This operation produces 3-channel kernels for sparkle and glow effects. It is typically used in conjunction with ConvolveSelective and ConvolveTrig.
Example
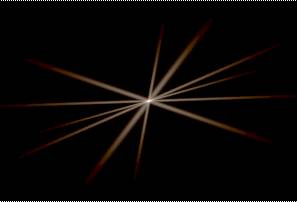
sizePoint = (300, 200) center = (150,100) slitAngle = 23 kind = ice.constants.SPARKLE_FRAUNHOFERSLITS p = ice.Sparkle(kind, sizePoint, center, ice.constants.FRACTIONAL, slitAngle)
